What is Value-Stream Mapping?
The lean methodology is a cyclic process via which the needs of customers are identified, then subsequently built into manufacturing or service processes in order to satisfy these critical requirements. As the old adage goes: “The customer is always right!”. The customer is king, and if they feel that their voices are not being heard, they can easily transfer their business elsewhere. To ensure customer satisfaction, the Lean Management tool Value Stream Mapping is utilized.
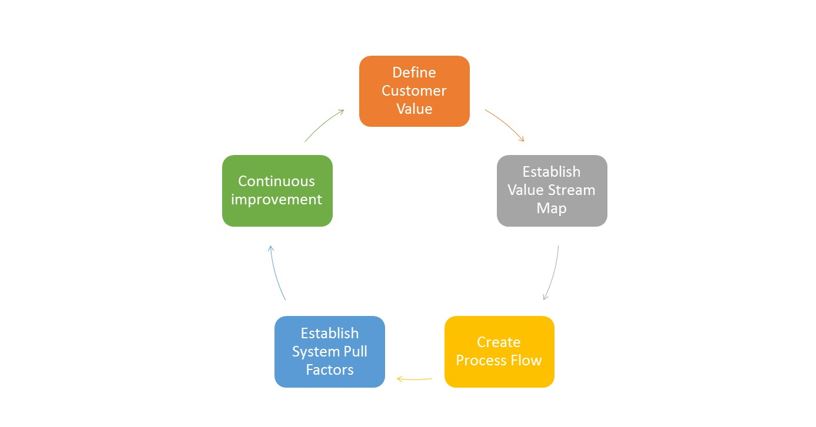
The Value-Stream mapping process assesses current system conditions, and facilitates the optimization of such systems into future states of perfection. The overall iterative improvement process is highlighted in Image 1 above.
Applications of Value-Stream Mapping
Value-Stream Mapping has various uses, and facilitates the optimization of various service and manufacturing systems in order to facilitate the elimination of waste. The applications include:
- Healthcare System optimization to facilitate quality improvement
- Logistics System optimization to facilitate product delivery
- Supply Chain System optimization to facilitate production efficiency improvement
- Software Development, to facilitate customer satisfaction
Value-Stream Map Creation
Creating a Value-Stream Map, like most lean activities, is a team activity. The process involves persons who are intimately involved with the current process under analysis, and a fresh set of eyes, who can identify opportunities not captured by the current system users. The Value-Stream Map outlines your process flow in a visual format. For those familiar with the SIPOC document, it outlines in a step by step format, what the flow is from supplier to customer. The visual representation of this process flow is the Value Stream Map. Visualizing the system is an ideal way to identify critical controls.
Creating a Value-Stream Map Template
Critical Value-Stream Map components:
- Process Facilitator
- Process Representatives
- Critical Process Mapping Utensils: Paper (A3 size), Post Its, Pencils/Markers, appropriate work area.
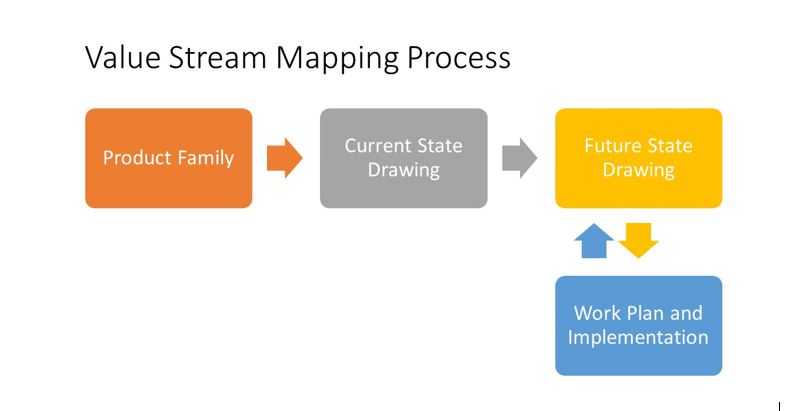
The Value Stream Mapping Process is outlined below.
Step 1: Product Family Selection
Product Family creation involves the establishment of a two priority matrix. The vertical axis can be a parameter such as Product/Service, with the appropriate listing outlined. The horizontal axis can be an outline of the critical process equipment that is used to manufacture/generate that product or service.
The whole idea is establish what the strategic vision for the product/service generation will be. In the process, you can decide to focus on a single product/service and its associated manufacturing/service process, or a product/service family or grouping and their associated processes. The voice of the customer will help you to establish what the process priorities should be.
Step 2: Creation of the Value Stream Map: Current State
After identifying the product/service or product/service family, the next steps would be visual generation of the processes that are create these items. Typically, standard process symbols are used to create these visuals, and map out the flow from supplier to customer. You are also free to be creative, and use your own pre-identified icons that are representative of your process.
Create appropriate boundaries, so that the appropriate levels of detail can be created from process start to process finish. Following the boundary creation, utilize your various symbols in order to create the process map in a series of sequential steps from supplier to customer. The steps are surface steps, and overall processes, not the finer process details.
Once the critical overall unit process/service operations are identified, map out the critical information flows from one stage to the next. Typically in operations, solid lines indicate material flows, while a dotted line will include an information flow. The information flows can include:
- Transaction points such information exchanges or purchases
- The Frequency of an action
- Communication processes between customers and suppliers
Step 2B: Process Data Analysis
Process Data Analysis is best collected in order to establish a current system condition for the parameters being analyzed. The focus differs for products and services, so ensure that the critical process parameters, which are typically identified from the Voice of the Customer, are measured. Place the critical values on the Value Stream Map, so that appropriate flows can be easily seen.
Process timing is also critical, in order to identify process bottlenecks.
Step 3: Value Stream Map Creation – Process Future State
The establishment of a Value Stream Map current condition, sets the stage for the Future Condition of the assessed system with respect to material and information flows. The customer is king, so the organization should now make reference to the customer’s requirements, and identify if the process is able to meet these requirements. Any process/information bottlenecks, can be easily identified by comparing the current process performance to the customer’s demands.
Step 4: Work Plan and Implementation
If there are any deviations, an appropriate target Value Stream with either the same process, with improved parameters can be generated, or with appropriate optimizations included in the process flow.
Following the identification of the ideal condition, create an appropriate action plan to bridge the transition between your Current Condition and the Target Condition. This can be in a simple table with an appropriate action plan, responsible party, and their associated time frame for execution.
Executing the previously mentioned four action steps will guarantee an appropriate Value-Stream Map Generation, and allow appropriate customer satisfaction to be built into your process flow. The aim is to eliminate muda or waste, and seeing the inefficiencies helps that ultimate accomplishment. Value Stream Mapping helps to accomplish this objective.