We can start this article explaining in a very simple way LEAN Operations, we can define it as a management model focused on the creation of flow to be able to deliver the maximum value for the clients, using for it the minimum and necessary resources. Where the creation of flow focuses on the reduction of the eight types of “waste” in products and services: Over-production, waiting time, transportation, excess processing, inventory, movements, defects and underutilized human potential.

If we can show in a graphic way each of the stages of this methodology we can refer to Form 1.
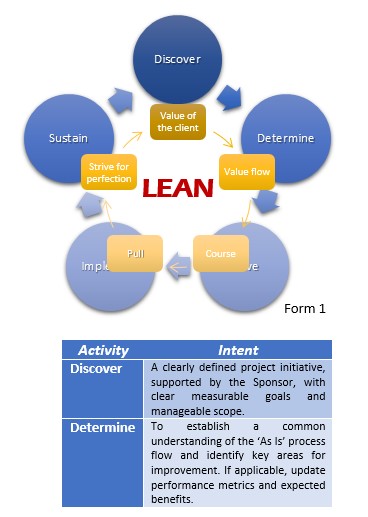
We can go into detail of the different activities that we must develop with each of the stages of this wonderful world of LEAN Operations.
As we already introduced it, our first stage is Discover, today we will stop to describe this interesting stage describing each task with its respective activities to drive:
1. Assess environmental readiness and current capabilities
a. Measure change readiness & capability: We must be very clear about the limits and scope when it comes to implementing this improvement. It is recommended to focus on the most critical Departments or Areas for the institution, but this depends a lot on the current institutional Vision.
b. Identify implications for a Lean Operations initiative: we must be clear about the benefits and know what could be the different scenarios where other areas could be benefited with these changes and some of the tasks that were done would stop doing for the good of the institution.
2. Define current process management maturity.
a. Measure current Business Project Management maturity: In order not to interrupt the commercial operation of the institution, it is important to bear in mind that businesses could be affected in their response times by being involved at some point in the identification and implementation of improvements.
b. Identify key implications for a Lean Operations initiative: Remember that in order to have a much more effective improvement implementation it is necessary to identify which are the key activities and tasks that will be benefited. We can not fix everything at once for being too much effort and low productivity or final result.
3. Define target entity.
a. Describe the target entity: The definition of the scope of each initiative of LEAN Operations is vital for the success of this methodology and where all the areas involved must be clear to promote as synergy.
b. Conduct process activity analysis: It is vital to map the current state of the productive processes in order to identify in an easier way the tasks that add value and which do not.
4. Select target process for improvement.
a. Identify Lean Operations process target: With a clearer picture of which activities add value and which do not, you can set priorities for their optimization.
b. Define target process: In this step it is necessary that both the process owner and the sponsor are aligned.
c. Confirm Process Owner: We must have the confirmation of the owner of the process about the identified and graphed to determine if everything related to the process analyzed has been included.
5. Determine Customer Experience
a. Identify key customer’s of target process: In order to improve customer service, it is necessary to determine the key processes to be improved in the area under analysis for optimization.
b. Obtain customer experience feedback: A variable is to know the opinion of the clients. To do this, you can select the most representative clients and know their opinion about what they perceive of the company and what their satisfaction is.
c. Summarize customer experience and needs: It is necessary to group all the needs of our clients and their sense of the attention that is being provided to optimize and provide a better experience with the vision of the institution.
6. Establish baseline performance
a. Identify performance for all dimensions: It is essential to be clear that other areas may be affected with any change to be made. In other words, to know the in-puts and out-puts of the entire productive line of our process.
b. Identify measurement gaps: As in any project, there are some risks or difficulties, which is why it is necessary to identify them and establish an action to respond to each eventuality. The more control you have of the project, the result and delivery time will be more successful.
c. Establish performance targets: In the case of the processes to be improved to allow a better approach and a better deliverable, the phrase “less is better” is applied, that is, less objectives to be pursued in order to focus all the institutional effort to the task.
d. Quantify performance in financial terms: A very important fact about this methodology is that apart from looking for process optimization and its execution, it is vital to focus on measuring savings economically and make the operation much better, saving time and money for the company.
7. Prepare for stage gate review
a. Summarize key learnings of the team: Each of the phases is a learning cycle for the entire work team, so it is important to point out the difficulties encountered and their resolution. The above creates a stronger bond between all the direct members in the execution of the Project.
b. Confirm Initiative Brief with Sponsor: The sponsor forms a very important role, given that without it this initiative would not be promoted, so you should be aware of a very executive way of the project and its progress.
8. Complete stage gate review
a. Complete corrective actions as required: Last but not the least is to make any adjustments in the work team or the management of identified risks to be able to correct and strengthen, to make way for the next step of this exciting methodology.
