Group technology is a theory of management based on the principle that “similar things should be done similarly”. It can be applied to various administrative activities including activities involved in manufacturing. Frederick Taylor initiated group technology as a manufacturing philosophy in 1919 that uses the similarities of produced parts in order to create the factory and shop floor layout design. Cellular manufacturing uses the principle of group technology by grouping parts with similar characteristics into part-families and corresponding machines into machine cells in order to achieve higher production efficiency compared to traditional manufacturing. Cellular manufacturing is an integral part of lean manufacturing.
There are three types of manufacturing systems namely job shop manufacturing, flow line manufacturing and cellular manufacturing.
Cellular manufacturing as shown in figure 1 is a hybrid system which links the benefits of both job shop manufacturing and flow line manufacturing. It is more cost-effective to manufacture parts having medium volume and medium variety.
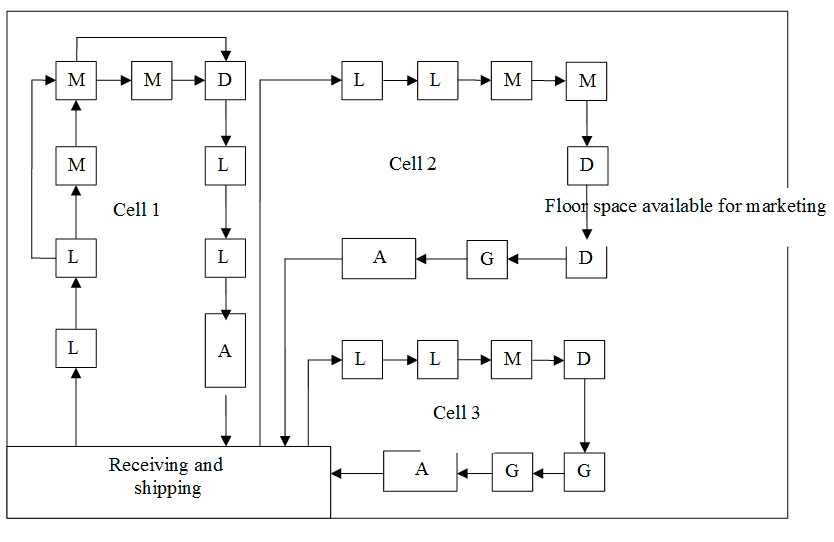 Figure 1: Cellular Manufacturing
Figure 1: Cellular Manufacturing
Cellular manufacturing considerably reduces total manufacturing cost, time and area of manufacturing industries. Manufacturing industries who adopt cellular manufacturing get improvement in profit, productivity and production quality. Cellular manufacturing also helps manufacturers in defeating their competitors in global business scenario. If manufactures implement cellular manufacturing system in their manufacturing industries then they can fully satisfy their customers by selling high quality products quickly in reasonable price.
Cellular manufacturing can be implemented in four stages as per the following:
- Cell formation: Grouping parts into part families and corresponding machines into machine cells by using the parts production process.
- Intra-cell layout: Layout of machines within each cell.
- Inter-cell layout: Layout of cells within the factory or shop floor.
- Scheduling: Scheduling of jobs in each cell.
In cellular manufacturing, Objective of machine layout is to minimize the intra-cell movement of various parts within the cell and it is obtained by properly arranging machines within the cell. Objective of cell layout is to minimize the inter-cell movement within the floor space and it is achieved by properly arranging cells within the factory or shop floor.
Cell formation, machine layout and cell layout problem in cellular manufacturing system are known to be NP-Complete optimization problems. Exact solution methods are inefficient for solving these large-sized NP-Complete problems. So heuristics, meta-heuristics and hybrid methods to solve these large-sized NP-Complete problems efficiently have been developed by researchers. Most popular meta-heuristics to solve these large-sized NP-Complete problems efficiently include genetic algorithm, simulated annealing, ant colony optimization and tabu search.
Appropriate performance criteria to compare performance of various methods to solve cell formation problem are grouping efficiency, grouping efficacy, machine utilization, bond energy, comparison with optimum solution, percentage of exceptional elements, number of inter-cellular moves, number of non-dominated solutions, hyper area ratio metric, quality metrics, spacing metric, relative metric, overall flow index, cell flow index and average cell flow index.
Appropriate performance criteria to compare performance of various methods to solve machine layout problem are total distance travelled by all parts, percentage of variation with optimum solution, price of a layout, cell flow index and average cell flow index. Appropriate performance criteria to compare performance of various methods to solve cell layout problem are percentage of deviation with best-known solution, total inter-cell material handling distances and overall flow index.
