When there is a requirement for major improvement in key business areas, translating into more that 50 percent to 95 percent improvement, then breakthrough improvement strategies are adopted in Six Sigma implementation and change methodology.
A Cross functional team consisting of five to seven members including six sigma black belts and green belts, is given the task of removing chronic problems affecting quality. Such projects are selected by the senior management team which also acts as a steering group.
The time frame for this major improvement is usually from four to twelve months, and is taken on as a special and temporary project and the scope of investigation and research spans across multiple functions of an organization. The focus of the team is a complete process or a product. A few projects in special focus areas are chosen which have the potential to yield maximum benefit in terms of productivity or quality improvement.
Design for Six Sigma (DFSS) projects are usually targeted for breakthrough improvements. They use the methodologies of DMADV and IDOV.
DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify)
It is a data-driven quality strategy for designing products and processes, and is part of a Six Sigma Quality Initiative. DMADV consists of five phases: Define Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify.
- Define the project goals and customer (internal and external) requirements.
- Measure and determine customer needs and specifications; benchmark competitors and industry.
- Analyze the process options to meet the customer needs.
- Design (detailed) the process to meet the customer needs.
- Verify the design performance and ability to meet customer needs.
IDOV (Identify, Design, Optimize, Validate)
It is used in DFSS for design and product optimization. An explanation of steps and practices used in IDOV stages are given below
- Identify the customer and specifications, Critical to Quality (CTQ). Voice of Customer (VOC), Technical requirements & quality targets
- Design translates the customer CTQs into functional requirements and into alternative solutions. The selection process cuts down the list of solutions to the “best” solution. Evaluate system concepts, Critical to Quality points, develop transfer functions, relating the CTQs to design
- Optimize uses advanced statistical tools and modeling to predict as well as optimize the design and performance. Robust design, Design Failure Mode, Predict Reliability, predict quality level, Optimize 6 sigma
- Validate makes sure that the design you have developed will meet the customer CTQs. Test and validate prototypes, , iterate design if required, assess performance and reliability
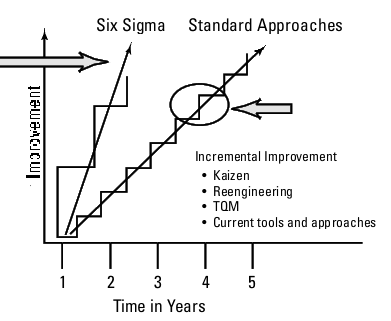
As can be seen from the drawing above, whereas traditional improvement approaches aim for gradual improvement in small steps over a long period of time, Breakthrough Improvement strategies aim for a radical improvement.
However, a Kaizen Blitz and Kaikaku are somewhat similar to Breakthrough Improvement as all of them aim for radical change.
A Kaizen Blitz is defined as a sudden overpowering effort to take something apart and put it back together in a better way. Usually a process, system, product or service is taken apart.
Kaikaku is a rapid change event and revolutionary while Kaizen is composed of smaller incremental changes and is evolutionary.
