Axiomatic Design is a design concept that was introduced by Nam Pyo Suh who works at MIT, United States. It proposes a systematic approach for the design of products, processes, components, software etc. It applies a scientific approach for designing products according to customer needs. The below are the two main concepts of Axiomatic Deign:
1. It is based on a four level design process and the four levels are zig-zagged for an optimal design (excepting customer requirements)
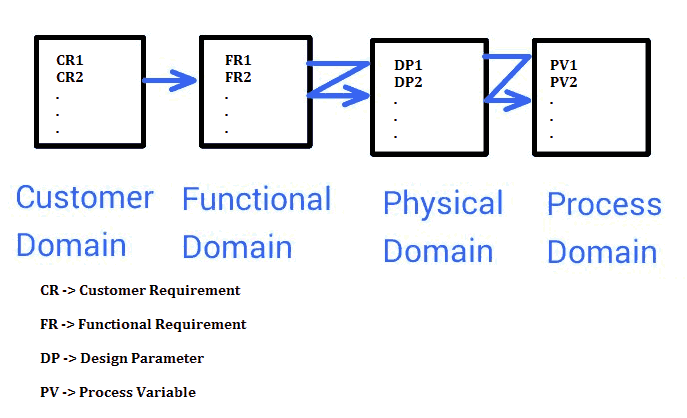
As explained in the figure, all Customer requirements are listed individually and split to lower levels as required. Each requirement should be addressed by one or more functional requirements. A Matrix is designed to represent the relationship between the two domains. Similarly, functional requirements are then converted into design parameters and into Process Variables subsequently. Based on the scope and applicability the design parameters are modified to suit the process variables and Functional requirements as per the Design parameter. This is known as Zig-zagging.
2. It has Two axioms at its base for each deign feature.
a. Axiom 1: Independent Axiom: This axiom is the key for the entire design. It maintains the independence of the Functional requirements, thereby ensuring that none of the requirements are compromised or left out. It ensures a complete and robust design of the product.
b. Axiom 2: Information Axiom: It minimizes the information content. Among various alternatives available to satisfy Axiom 1, this axiom chooses the one with minimum information, and thus ensures to get an optimal design cost and a simple product.
The above two concepts are the core for the success of Axiomatic design. Axiomatic design I proved to address the issues of Taguchi methods. Thus it is used across industries to design a complete product with optimal cost that is simple and user-friendly and in a minimal time by eliminating trial and error methods.
